|
BioDiscovery : Research Article
|
|
Corresponding author: Vladimir Kulchitsky (vladi@fizio.bas-net.by)
Academic editor: Nikolai Zhelev
Received: 30 Jun 2017 | Accepted: 08 Aug 2017 | Published: 18 Oct 2017
© 2017 Khalil L. Gainutdinov, Svetlana G. Pashkevich, Vyatcheslav V. Andrianov, Guzel G. Yafarova, Margarita O. Dosina, Tatiana Kh. Bogodvid, Julia P. Stukach, Dinara I. Silant'eva, Aleksandra S. Zamaro , Timur V. Sushko, Vladimir Kulchitsky
This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY 4.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Citation: Gainutdinov K, Pashkevich S, Andrianov V, Yafarova G, Dosina M, Bogodvid T, Stukach J, Silant'eva D, Zamaro A, Sushko T, Kulchitsky V (2017) Participation of NO-synthase in Control of Nitric Oxide Level in Rat Hippocampus after Modelling of Ischaemic and Haemorrhagic Insult. BioDiscovery 20: e14810. https://doi.org/10.3897/biodiscovery.20.e14810
|
|
Abstract
Electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) was used as a method for recording the content of the nitric oxide (NO) in hippocampal tissues of intact rats and rats after modelling of ischaemic and haemorrhagic stroke. Based on direct measurements of NO by EPR spectroscopy, it was shown that, within 5 hours after the onset of symptoms of ischaemic and haemorrhagic stroke, the formation of NO in the hippocampus was reduced by a factor of 2-3 and this reduction was maintained for a period of between 24 and 72 hours. The results show that a systemic character of a decrease in the intensity of NO production during the modelling of ischaemic events in the brain reflects the effects of central dysregulation of the functions at the level of the whole organism such that it is appropriate to consider implementing the correction of the vital systems of the body in a stroke. It has indicated that non-selective NO-synthase blocker L-NAME reduced the low level of NO production by a factor of 3 by its administration within 72 hours after post-ischaemic and haemorrhagic stroke. It was discovered however that L-NAME returns the level of NO production to baseline (control) by its administration within 5 hours after ischaemia.
Keywords
Nitric oxide, Electron paramagnetic resonance, Spin trap, Ischaemic brain stroke, Haemorrhagic brain stroke
Introduction
There appears to be increasing evidence about the impact of regulatory substances of intestinal microflora on the functional state of the brain of animals (
In the vital functions of animals, the role of NO is especially significant in the cardiovascular function (
Material and Methods
Experimental protocol. Simulation of ischaemic and haemorrhagic stroke in rats and application of trapping for nitric oxide
Modelling of ischaemic and haemorrhagic stroke was produced on rats in the Institute of Physiology of NAS of Belarus, Minsk. Animals were kept in standard vivarium conditions (12/12- light and dark rhythm, air temperature of 23±1°C and stable supply and exhaust ventilation) with free access to water and food (ad libitum) and a diet in accordance with the standards for keeping laboratory animals. For the modelling of ischaemic stroke, animals were subjected to 5-minute hypoxia (conditional rise to a height of 4500m above sea level which corresponded to a pressure of 432mmHg and a decrease in oxygen partial pressure pO2 from 159mmHg to 90mmHg on average) (
Formation of the complex of NO with the spin trap in rat tissues
The difficulty in determining the maintenance of the free NO in the tissues of the organism is due to its short lifetime which appears in low concentrations in tissues. Recently, one of the most effective methods for the detection and quantification of NO in biological tissues is the method of electron paramagnetic resonance (
Statistical processing of experimental results
The results are shown as mean ± SEM. The unpaired Student’s t-test and non-parametric Mann–Whitney test were used for comparison between two groups. One-Way ANOVA followed by the Tukey post-hoc test and a repeated Two-Way ANOVA were used for comparison between statistical groups. The statistical software SigmaStat32 was used. The statistical significance criterion was p<0.05.
Results
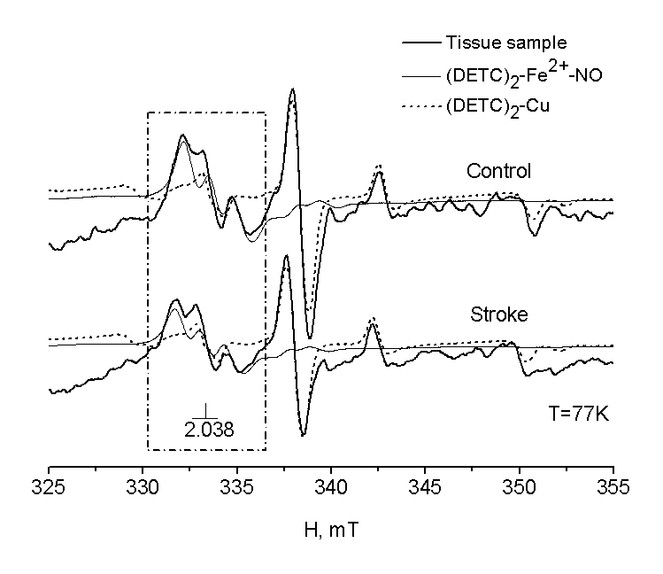
EPR spectra of the hippocampus of intact rats and rats after modelling of haemorrhagic stroke
Fig.
Dynamics of the maintenance of NO in the hippocampus after modelling ischaemic and haemorrhagic stroke
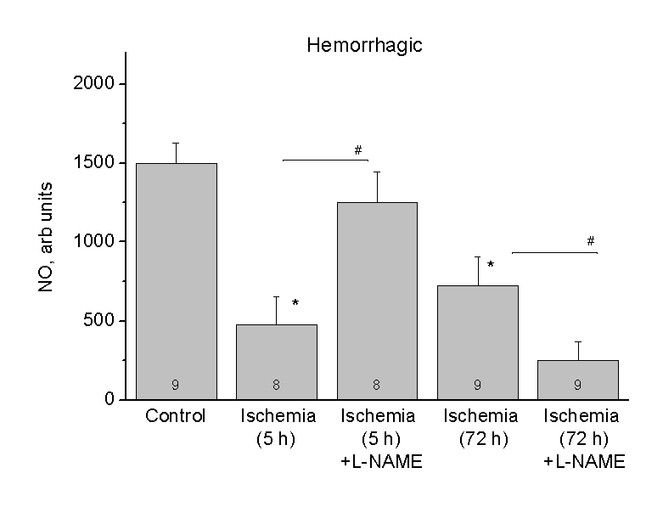
Fig.
The relative content of NO in the hippocampus of healthy rats (Control) and rats after 5 (Ischaemia, 5h) and 72 (Ischaemia, 72h) hours of the haemorrhagic stroke and also after using of inhibitor L-NAME (Ischaemia, 5h + L-NAME) and (Ischaemia, 72h + L-NAME) respectively. The ordinates axis is the average integral intensity of the signal.
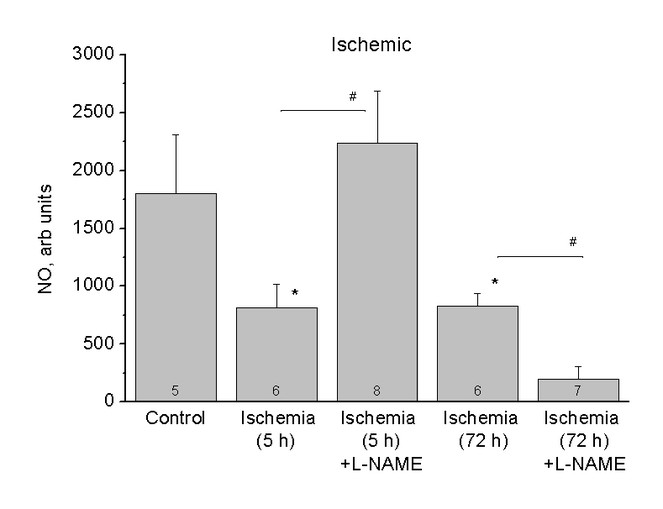
Fig.
The relative content of NO in the hippocampus of healthy rats (Control) and rats after 5 (Ischaemia, 5h) and 72 (Ischaemia, 72h) hours of the ischaemic stroke and also after using of inhibitor L-NAME (Ischaemia, 5h + L-NAME) and (Ischaemia, 72h + L-NAME) respectively. The ordinates axis is the average integral intensity of the signal.
The dynamics of the NO maintenance in the hippocampus after modelling of the ischaemic and haemorrhagic stroke with administration of the NO synthase blocker L-NAME
Taking into account that the NO may play a pathogenic role in a number of pathological conditions of the nervous system, including ischaemia, some NOS inhibitors have become the subject of intensive study as potential neuroprotective agents (
Discussion
Discussion of the design of experiment
The problem of cerebral ischaemia is most acute in the world (
Discussion of the results of experiment
At the present time, the development of cerebral ischaemia and the subsequent occurrence of stroke are associated with impaired cerebral blood flow, as well as with impaired regulation of the blood supply to the brain tissues by the system of NO (
Conclusion
Thus, the analysis of literature and the results of our experiments show the ambiguity of the data that reflects the well-known fact of dose-dependent effects of NO in the brain. In the present work, it was demonstrated that the process of the comprehensive approach and the application of precision methods for measuring NO levels made it possible to receive data for the dynamics of NO production in nerve tissue.
Acknowledgements
The work is performed according to the Russian Government Program of Competitive Growth of Kazan Federal University; by Russian Foundation for Basic Research (Grant No. 16-54-00098) and by Belarusian Republican Foundation for Fundamental Research (Grant B16R-166). The authors thank V.S. Iyudin for help in EPR measurements.
Author contributions
Khalil L. Gainutdinov carried out research using electron paramagnetic resonance and formalised the results of this section of the study. He formulated the conclusions of the work. Svetlana G. Pashkevich conducted experimental studies in rats and formalised the results of the study. Vyatcheslav V. Andrianov carried out research using electron paramagnetic resonance and formalised the results of this section of the study. Guzel G. Yafarova carried out research using electron paramagnetic resonance and formalised the results of this section of the study. Margarita O. Dosina conducted experimental studies in rats and formalised the results of the study. Tatiana Kh. Bogodvid carried out research using electron paramagnetic resonance and formalised the results of this section of the study. Julia P. Stukach conducted experimental studies in rats and formalised the results of the study. Dinara I. Silant'eva carried out research using electron paramagnetic resonance and formalised the results of this section of the study. Aleksandra S. Zamaro conducted experimental studies in rats and formalised the results of the study. Timur V. Sushko conducted experimental studies in rats and formalised the results of the study. Vladimir Kulchitsky conducted experimental studies in rats and formalised the results of the study. He formulated the conclusions of the work.
Conflicts of interest
No potential conflict of interest was disclosed by any of the authors.
References
-
Changes of Nitric Oxide Content in the Rat Hippocampus, Heart and Liver in Acute Phase of Ischemia.Applied Magnetic Resonance47(9):965‑976. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00723-016-0815-3
-
Changes in nitric oxide in heart of intact and sympathectomized rats of different age.Russian Journal of Developmental Biology39(6):352‑356. https://doi.org/10.1134/s1062360408060040
-
Investigation by method of EPR of influence of hypoxia on nitric oxide (NO) production in blood of rats Krushinskii-Molodkina.Biophysica54(5):894‑899. [InRussian].
-
Roles of nitric oxide in brain hypoxia-ischemia.Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Bioenergetics1411:415‑436. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0005-2728(99)00030-4
-
Dinitrosyl iron complexes with glutathione as NO and NO+ donors.Nitric Oxide29:4‑16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.niox.2012.11.001
-
Increased nitric oxide-mediated neurotransmission in the medial prefrontal cortex is associated with the long lasting anxiogenic-like effect of predator exposure.Behavioural Brain Research256:391‑397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2013.08.006
-
Body Fluid Changes, Cardiovascular Deconditioning and Metabolic Impairment Are Reversed 24 Hours after a 5-Day Dry Immersion.Open Journal of Nephrology03(01):13‑24. https://doi.org/10.4236/ojneph.2013.31004
-
Inhibition of nitric oxide synthesis does not reduce infarct volume in a rat model of focal cerebral ischaemia.Neuroscience Letters142(2):151‑154. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-3940(92)90361-a
-
Stroke.The Lancet371(9624):1612‑1623. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(08)60694-7
-
Mechanisms of ischemic brain damage.Neuropharmacology55(3):310‑318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2008.01.005
-
Nitric Oxide and Mitochondrial Signaling: From Physiology to Pathophysiology.Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology27(12):2524‑2531. https://doi.org/10.1161/atvbaha.107.151167
-
NO-independent stimulators and activators of soluble guanylate cyclase: discovery and therapeutic potential.Nature Reviews Drug Discovery5(9):755‑768. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd2038
-
Nitric oxide synthases: regulation and function.European Heart Journal33(7):829‑837. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehr304
-
EPR study of nitric oxide production in rat tissues under hypokinesia.Biophysics58(2):203‑205. https://doi.org/10.1134/s0006350913020073
-
EPR Study of the Intensity of the Nitric Oxide Production in Rat Brain After Ischemic Stroke.Applied Magnetic Resonance40(3):267‑278. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00723-011-0207-7
-
Nitric Oxide Donors as Neuroprotective Agents after an Ischemic Stroke-Related Inflammatory Reaction.Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity2013:1‑16. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/297357
-
Nitric oxide metabolites in goldfish under normoxic and hypoxic conditions.Journal of Experimental Biology213(21):3593‑3602. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.048140
-
What Part of NO Don't You Understand? Some Answers to the Cardinal Questions in Nitric Oxide Biology.Journal of Biological Chemistry285(26):19699‑19704. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.r110.101618
-
Delayed reduction of ischemic brain injury and neurological deficits in mice lacking the inducible nitric oxide synthase gene.J Neurosci17(23):9157‑9164.
-
Use of Imidazoline Nitroxides in Studies of Chemical Reactions ESR Measurements of the Concentration and Reactivity of Protons, Thiols, and Nitric Oxide.Biological Magnetic Resonance.14. https://doi.org/10.1007/0-306-47072-1_4
-
LP63: The analysis of chemosensitive structures contribution to obstructive sleep apnea development.Clinical Neurophysiology125:S330‑S331. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1388-2457(14)51089-9
-
Inflammatory Cytokines in Experimental and Human Stroke.Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism32(9):1677‑1698. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.2012.88
-
Nitric oxide synthase in hypoxic or ischemic brain injury.Reviews in the Neurosciences26(1): . https://doi.org/10.1515/revneuro-2014-0041
-
Growing up in a Bubble: Using Germ-Free Animals to Assess the Influence of the Gut Microbiota on Brain and Behavior.International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology19(8):pyw020. https://doi.org/10.1093/ijnp/pyw020
-
Production and Storage of Nitric Oxide in Adaptation to Hypoxia.Nitric Oxide3(5):393‑401. https://doi.org/10.1006/niox.1999.0244
-
Inflammation Enhances the Risks of Stroke and Death in Chronic Chagas Disease Patients.PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases10(4):e0004669. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0004669
-
Complexes of Fe2+ with diethyldithiocarbamate or N-methyl-d-glucamine dithiocarbamate as traps of nitric oxide in animal tissues: comparative investigations.Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - General Subjects1336(2):225‑234. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0304-4165(97)00032-9
-
Transcriptome Analysis Identifies Key Metabolic Changes in the Hooded Seal (Cystophora cristata) Brain in Response to Hypoxia and Reoxygenation.PLOS ONE12(1):e0169366. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0169366
-
Nitric Oxide and Peroxynitrite in Health and Disease.Physiological Reviews87(1):315‑424. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00029.2006
-
Effect of dinitrosyl iron complexes with glutathione on hemorrhagic shock followed by saline treatment.European Journal of Pharmacology662:40‑46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2011.04.046
-
Nitric oxide and cycle in miocarde: molecular, biochemical and physiological aspects.Uspehi fiziologicheskih nauk38:39‑58. [InRussian].
-
Ongoing activity in trigeminal wide-dynamic range neurons is driven from the periphery.Neuroscience150(3):681‑691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.09.032
-
Nitric Oxide Synthase in Models of Focal Ischemia.Stroke28(6):1283‑1288. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.str.28.6.1283
-
Nitric oxide inhibition aggravates ischemic damage of hippocampal but not of NADPH neurons in gerbils.Stroke25(2):436‑443. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.str.25.2.436
-
Electron paramagnetic resonance study on nitric oxide production during brain focal ischemia and reperfusion in the rat.Brain Research647(1):91‑96. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-8993(94)91402-8
-
Nitric Oxide Signaling in Brain Function, Dysfunction, and Dementia.The Neuroscientist16(4):435‑452. https://doi.org/10.1177/1073858410366481
-
Nitric Oxide: Considerations for the Treatment of Ischemic Stroke.Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism32(7):1332‑1346. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.2012.12
-
Electron Paramagnetic Resonance (EPR) Detection of Nitric Oxide Produced during Forebrain Ischemia of the Rat.Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism14(5):715‑722. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.1994.92
-
Iron dithiocarbamate as spin trap for nitric oxide detection: Pitfalls and successes.Methods in Enzymology. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0076-6879(02)59169-2
-
Neuroprotection of Dexmedetomidine against Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Rats: Involved in Inhibition of NF-κB and Inflammation Response.Biomolecules & Therapeuticshttps://doi.org/10.4062/biomolther.2015.180
-
Inhibition of Nitric Oxide Synthesis Increases Focal Ischemic Infarction in Rat.Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism12(5):717‑726. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.1992.102
-
HMBG1 Mediates Ischemia—Reperfusion Injury by TRIF-Adaptor Independent Toll-Like Receptor 4 Signaling.Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism31(2):593‑605. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.2010.129
-
Cell adhesion molecules and ischemic stroke.Neurological Research30(8):783‑793. https://doi.org/10.1179/174313208x341085
-
Effect of NO Synthase Blockade on NO Production in Rat Heart under Conditions of Hypokinesia.Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine157(5):545‑547. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-014-2610-1